
What chips and electronic components are used in new energy vehicles? What do they control?
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
New energy vehicles (NEVs), including electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), rely on a wide range of chips and electronic components to manage and control various systems. These components are critical for ensuring efficiency, safety, and performance. Below is a breakdown of the key chips and components used in NEVs and their functions:
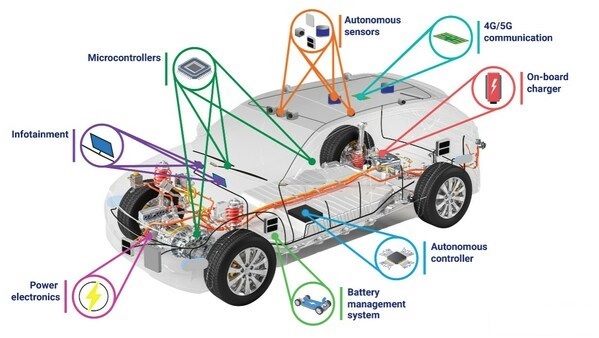
1. Microcontroller Units (MCUs) and Microprocessors
-
Examples: STM32, NXP S32K, Infineon Aurix, Texas Instruments TMS570.
-
Function:
-
Control the powertrain, including the electric motor and transmission.
-
Manage battery management systems (BMS).
-
Handle vehicle control units (VCUs) for overall system coordination.
-
Process data from sensors and execute control algorithms.
-
2. Power Management ICs (PMICs)
-
Examples: Infineon OPTIREG, Texas Instruments LM5170.
-
Function:
-
Regulate and distribute power to various subsystems.
-
Manage voltage levels for sensors, actuators, and control units.
-
Optimize energy efficiency and reduce power losses.
-
3. Battery Management System (BMS) Chips
-
Examples: Analog Devices ADBMS1818, Texas Instruments BQ76PL455A.
-
Function:
-
Monitor and balance individual cell voltages in the battery pack.
-
Ensure safe charging and discharging of the battery.
-
Provide thermal management to prevent overheating.
-
Estimate the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH).
-
4. Motor Control Chips
-
Examples: Infineon IMC300, STMicroelectronics STM32 FOC.
-
Function:
-
Control the speed, torque, and direction of the electric motor.
-
Implement field-oriented control (FOC) for efficient motor operation.
-
Interface with sensors (e.g., encoders, Hall effect sensors) for precise control.
-
5. DC-DC Converters
-
Examples: ON Semiconductor NCP1034, Maxim Integrated MAX20090.
-
Function:
-
Convert high-voltage DC from the battery to lower voltages for auxiliary systems (e.g., 12V or 48V).
-
Enable efficient power transfer between different voltage domains.
-
6. Inverters
-
Examples: Infineon HybridPACK, Mitsubishi Electric J1 Series.
-
Function:
-
Convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the electric motor.
-
Use insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) or silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs for high-efficiency switching.
-
7. Sensors
-
Examples:
-
Current Sensors: Allegro ACS712, LEM LAH 50-P.
-
Temperature Sensors: NTC thermistors, Texas Instruments TMP117.
-
Position Sensors: Hall effect sensors, encoders.
-
-
Function:
-
Monitor current, voltage, temperature, and position for motor and battery systems.
-
Provide feedback for control algorithms.
-
8. Communication Chips
-
Examples:
-
CAN Transceivers: NXP TJA1050, Texas Instruments TCAN332.
-
Ethernet PHY: Microchip LAN8742A.
-
Wireless Modules: ESP32, Quectel BG96 (for IoT connectivity).
-
-
Function:
-
Enable communication between electronic control units (ECUs) via CAN bus, LIN bus, or Ethernet.
-
Support vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication for connected vehicles.
-
9. Gate Drivers
-
Examples: Infineon EiceDRIVER, Texas Instruments UCC27531.
-
Function:
-
Drive the gates of power transistors (e.g., MOSFETs, IGBTs) in inverters and DC-DC converters.
-
Ensure fast and reliable switching of high-power devices.
-
10. Charging Control Chips
-
Examples: STMicroelectronics STBC08, Texas Instruments UCC28740.
-
Function:
-
Manage AC/DC charging processes.
-
Support fast charging protocols (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO).
-
Ensure safe and efficient charging of the battery.
-
11. Display and HMI Controllers
-
Examples: NXP i.MX, Renesas R-Car.
-
Function:
-
Drive the infotainment system and dashboard displays.
-
Process touch inputs and provide user interfaces.
-
12. Safety and Security Chips
-
Examples: Infineon OPTIGA, NXP A1006.
-
Function:
-
Ensure functional safety (e.g., ISO 26262 compliance).
-
Provide secure communication and authentication (e.g., for over-the-air updates).
-
13. Passive Components
-
Examples:
-
Capacitors: Ceramic, electrolytic, and film capacitors.
-
Inductors: Power inductors for filtering and energy storage.
-
Resistors: Current sensing and voltage division.
-
-
Function:
-
Filter noise and stabilize power supplies.
-
Provide energy storage and current limiting.
-
14. Advanced Components
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) Devices:
-
Examples: Cree Wolfspeed SiC MOSFETs, GaN Systems GS66508B.
-
Function:
-
Enable higher efficiency and power density in inverters and converters.
-
Reduce heat dissipation and improve range.
-
-
What These Components Control
-
Powertrain:
-
Electric motor control, torque management, and regenerative braking.
-
-
Battery System:
-
Charging, discharging, and thermal management.
-
-
Vehicle Dynamics:
-
Stability control, traction control, and anti-lock braking systems (ABS).
-
-
Infotainment:
-
Navigation, entertainment, and connectivity.
-
-
Safety Systems:
-
Airbag control, collision detection, and driver assistance systems (ADAS).
-
-
Auxiliary Systems:
-
Lighting, climate control, and power windows.
-
Key Trends in NEV Electronics
-
Integration: Combining multiple functions into a single chip (e.g., system-on-chip for motor control).
-
High Voltage: Supporting higher voltage levels (e.g., 800V systems) for faster charging and improved efficiency.
-
Connectivity: Enabling V2X communication and over-the-air updates.
-
Sustainability: Using eco-friendly materials and improving energy efficiency.
By leveraging these chips and components, new energy vehicles achieve high performance, safety, and efficiency, paving the way for the future of transportation.
