
Unveiling the Difference Between DSP VS ARM
September 08 2023  1279
1279
Inquiry
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
QUICK RFQ
ADD TO RFQ LIST
In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between DSP VS ARM, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. We will also look at some of the application examples where DSP and ARM are used.
What is a Digital Signal Processor (DSP)?
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a customized microprocessor chip, with an architecture tailored to the practical requirements of digital signal processing. On MOS-integrated circuit devices, DSPs are produced. They are frequently utilized in high-definition television (HDTV) products, mobile phones, disk drives, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar, and speech recognition systems.
What is an ARM Processor?
ARM processors, a family of central processing units (CPUs), are built on the RISC (reduced instruction set computing) architecture. Advanced RISC Machine is the name of the technology. When compared to more well-known server architectures like x86, ARM architectures provide a distinct approach to how the hardware for a system is created.
What are the Differences Between DSP and ARM?
Themain difference between DSPs and ARM processors is their areas of focus. While ARM processors are more general-purpose processors, DSPs are made primarily for digital signal processing. This indicates that a variety of DSP properties, such as the following, are optimal for digital signal processing:- High-speed calculators
- Hardware that supports floating-point computation
- Parallel data channels in many
- Customizable memory
| Feature | DSP | ARM Processor |
| Focus | Digital signal processing | General-purpose |
| Arithmetic units | High-speed | Less powerful |
| Floating-point arithmetic | Hardware support | Software emulation |
| Parallel data paths | Multiple | Single |
| Programmable memory | Yes | No |
| Power consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Video related to DSP VS ARM
Advantages and Disadvantages of DSP and ARM
Advantages of DSP
- Digital systems in DSP can be cascaded without encountering any loading issues.
- In this way, digital circuits may be quickly and cheaply replicated in vast quantities.
- Digital circuits are less susceptible to component value tolerances.
- Because the digital signals can be processed offline, these can be transmitted conveniently.
- A digital programmable system's program can be updated to alter the operations involved in digital signal processing.
- Compared to analog systems, it is easier to control accuracy with digital systems.
- By using DSP technology, complex signal processing algorithms can be built.
- Magnetic media, such as magnetic tape, may easily store digital signals without sacrificing the signal's quality of reproduction.
Disadvantages of DSP
- Anti-aliasing filters must be used before the analog to digital converter (ADC) and reconstruction filters must be used after the digital to analog converter (DAC) when utilizing DSP. The incorporation of these two additional modules, ADC and DAC, enhances the complexity of DSP-based electronics.
- High-speed digital signal processing, or DSP, uses more top internal hardware resources to process the signal.
- Each DSP has a unique hardware design and set of software commands.
- Given that the majority of DSP chips are quite expensive, one should employ them with caution according to the hardware and software requirements.
- The detection of digital signals is only possible in synchronized communication networks; it is not possible in analog systems.
Advantages of ARM
- Cost-effective to produce: The ARM Processor is particularly cost-effective to produce because it does not require expensive machinery. It is produced for a substantially lower cost as compared to other processors. They are therefore suitable for producing inexpensive mobile phones and other electronics.
- Work More Quickly: ARM only does one operation at once. This speeds up its operation. It features a speedier response time and decreased latency.
- Better Battery Life: The battery life of ARM processors is better. This is evident while managing both ARM-based and non-ARM-based devices. Those who worked on ARM processors put in more hours and were let go later than those who did not.
- Load store architecture: To minimize memory interactions, the processor uses a load store architecture that stores data in a variety of registers. To move data from external memory to the register bank, it has distinct load and store instructions.
- Power effectiveness: ARM processors are made with power efficiency in mind, which is crucial for mobile devices whose battery life is constrained.
Disadvantages of ARM
- Some processors have speed limitations, which could be problematic.
- When using ARM processors, scheduling instructions might be challenging.
- The programmer must execute instructions correctly. This is because the execution of them determines the total performance of ARM processors.
- Programmers with extreme skill are required for ARM processors. This is due to the significance and complexity of execution (a processor performs worse when improperly performed).
- Limited performance: ARM processors may not have the same processing capability as other processor types, which may affect their capacity to execute more demanding programs.
- Compatibility: The range of programs that can be operated on ARM-based devices may be constrained by the incompatibility of some software with ARM processors.
- Limited multitasking: ARM processors may not multitask as effectively as other processor types, which may restrict their capacity to run numerous applications at once.
- Limited program support: Some software may not be ARM processor-optimized, which might cause compatibility problems and performance restrictions.
What is DSP used for?
- Audio and video processing: DSPs are employed in applications for filtering, compression, and noise reduction in audio and video processing.
- Communications: In communications applications, DSPs are used to carry out operations including modulation, demodulation, and error correction.
- Control systems: DSPs are employed in applications involving control systems to carry out functions including feedback control and signal conditioning.
- Medical imaging: DSPs are employed in applications for medical imaging to carry out functions including image reconstruction and filtering.
- Radar and sonar: DSPs are employed in the signal processing, target detection, and tracking functions of radar and sonar applications.
- Wireless networking: DSPs are used to carry out operations including modulation, demodulation, and error correction in wireless networking applications.
- Signal filtering: DSPs are used to handle tasks like eliminating noise and interference from signals in signal filtering applications.
- Speech recognition: DSPs are utilized in speech recognition applications to carry out tasks like turning speech into text.
What is ARM used for?
- Tablets and smartphones: The great majority of tablets and smartphones use ARM CPUs. Due to its low-power and energy-efficient design, ARM processors are advantageous for mobile devices.
- Servers: ARM processors are being used in servers more and more. This is due to ARM processors' increasing power and ability to meet the requirements of server workloads.
- Networking equipment: A wide range of networking hardware, including routers, switches, and firewalls, uses ARM processors. This is due to the fact that ARM processors are made to be affordable and easily scalable to fit the requirements of various applications.
- Industrial control systems: Systems for controlling manufacturing facilities, electricity grids, and other industrial processes use ARM CPUs. Because they are built to be dependable and resistant to severe environments, ARM processors are the reason for this.
- IoT devices: A wide range of IoT devices, including wearables, smart homes, and industrial sensors, all employ ARM CPUs. Due to their tiny size and low power consumption, ARM processors are ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Automotive electronics: Electronics used in automobiles, such as infotainment systems and driver assistance systems, are increasingly using ARM CPUs. This is so that they may be easily integrated into automobiles and since ARM processors are made to be energy-efficient.
Examples of a DSP
- Texas Instruments TMS320C6000 family: This DSP family is utilized in a wide range of applications, including communications, control systems, and audio and video processing.
- Analog Devices Blackfin family: This DSP family is renowned for its great performance and low power consumption, and it is employed in a wide range of applications.
- Freescale PowerPC e500 family: Freescale Family of DSPs known as the PowerPC e500 is used in industrial control systems and other applications that demand great performance and dependability.
- ARM Cortex-A family: This group of processors is utilized in a wide range of products, such as servers, smartphones, and tablets. Some ARM Cortex-A processors contain DSP extensions that make them appropriate for use in applications involving digital signal processing.

- FPGAs: Although FPGAs are not technically DSPs, they can be configured to carry out tasks related to digital signal processing. Applications that value flexibility and customizability frequently use FPGAs.
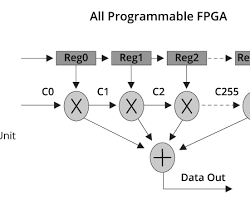
Examples of an ARM
- Cortex-A: The Cortex-A family of ARM processors is the most widely used family. Numerous programs, such as those for servers, smartphones, and tablets, use it. High performance and low power consumption are hallmarks of the Cortex-A series of processors.
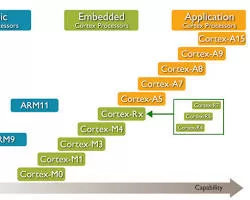
- Cortex-M: The Cortex-M family is intended for use in microcontroller applications. It is renowned for using little electricity and being compact. Wearable electronics, Internet of Things gadgets, and commercial sensors all employ the Cortex-M family of processors.
- Cortex-R: Real-time applications are catered for by the Cortex-R series. It has a low latency and deterministic performance. Applications for the Cortex-R series include industrial control systems, medical devices, and automotive electronics.

- Cortex-A55: Designed for mobile applications, the Cortex-A55 is a high-performance, low-power processor. It has a number of new features, including a 16-way superscalar pipeline and a new branch prediction unit, and is based on the ARMv8-A architecture.
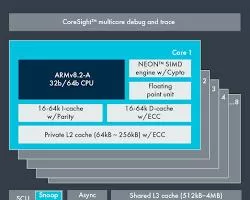
- Cortex-X1: The most potent ARM processor to date is the Cortex-X1. High-performance applications like gaming and artificial intelligence are intended for it. Numerous new capabilities, including a 32-way superscalar pipeline and a redesigned cache hierarchy, are present in the Cortex-X1.

Conclusion
Both digital signal processors (DSPs) and ARM processors are significant processor subtypes that are utilized in a wide range of applications. In contrast to ARM processors, which are more general-purpose processors, DSPs are created primarily for the processing of digital signals. The specific application determines which processor type should be used.Populer Posts
EP4CGX150DF27C7N
Intel
M2GL010T-VF256
Microchip Technology
10AX090N4F45I3LG
Intel
A1415A-PQ100C
Microsemi Corporation
1SG280HU3F50I2VG
Intel
A3P400-2FG256I
Microchip Technology
10AX090U2F45I1SG
Intel
10AX115U2F45E2LG
Intel
5CGTFD5C5M13I7N
Intel
10M16SLY180I8G
Intel
10AX032E4F29I3LG
Intel
