
Diode Basis: Symbol, Types and Applications
August 29 2023  1169
1169
Inquiry
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
QUICK RFQ
ADD TO RFQ LIST
Diodes are essential components in electronics, serving important functions such as rectification, modulation, regulation, and protection. They come in various types and are represented by different symbols. This blog covers the basics of diodes and their common applications.
What is A Diode?
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component made of semiconductor material, such as silicon or germanium, that allows the flow of electric current in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. When voltage is applied in the forward bias direction, the diode acts as a closed switch with minimal resistance, while in the reverse bias direction, it acts as an open switch with high resistance. Diodes are used in rectification circuits, voltage regulation, signal modulation, and protection circuits, as well as in semiconductor devices like transistors and integrated circuits.Diode Symbol and Structure
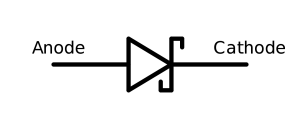
The symbol of a diode consists of a triangle pointing towards a vertical line. The vertical line represents the cathode, and the triangle represents the anode. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of current flow when the diode is forward-biased.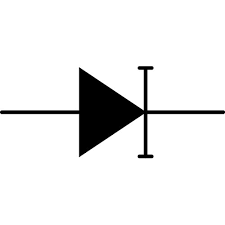
Types of Diode
Diodes are electronic components that allow the flow of electric current in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. There are several types of diodes, each designed for specific applications. Let's explore some commonly used diode types: Rectifier Diodes: Rectifier diodes are essential for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). They have a high forward current carrying capacity and are available in two main types:
- Standard Rectifier Diodes: These diodes have a low forward voltage drop and are commonly used in power supply circuits and rectification applications.
- Fast Recovery Rectifier Diodes: These diodes have a faster recovery time, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.




How Does A Diode Work?
A diode is an essential electronic component that serves the purpose of allowing the flow of electric current in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It functions as a unidirectional conductor, akin to a check valve in a plumbing system. When a diode is forward-biased, meaning the positive terminal of a voltage source is connected to the anode (positive terminal) of the diode, and the negative terminal is connected to the cathode (negative terminal), it permits current to flow freely through it. This behavior arises from the diode's unique construction, which facilitates the movement of electrons from the anode to the cathode. Conversely, when a diode is reverse-biased, with the positive terminal of the voltage source connected to the cathode and the negative terminal connected to the anode, it acts as a barrier to current flow. In this state, the diode effectively acts as an insulator, preventing the movement of electrons from the cathode to the anode. The primary function of a diode is to regulate the direction of current flow within a circuit. It finds wide-ranging applications, including rectification, voltage regulation, signal modulation, reverse polarity protection, and signal demodulation. Diodes are extensively used in electronic devices, power supplies, communication systems, and various other fields. In summary, the diode's capacity to permit current flow in one direction while hindering it in the opposite direction makes it an indispensable component in modern electronics. Its utilization enables the development of diverse electronic circuits and systems, thus contributing significantly to technological advancements.Applications of Diode
Diodes are widely used in electronics and electrical engineering due to their ability to control current flow. They are essential in many electronic circuits and systems. Common applications of diodes include: Rectification: Diodes are extensively used for rectification, where they convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). They achieve this by allowing current to flow in only one direction, effectively removing the negative portion of the AC waveform. Rectifier diodes are commonly used in power supplies and electronic devices to provide a stable DC voltage. Voltage Regulation: Zener diodes, a specific type of diode, are commonly used for voltage regulation. They are designed to maintain a constant voltage across their terminals, even when the input voltage changes. Zener diodes are used to stabilize power supplies, protect sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes, and create reference voltage sources. Signal Modulation: Diodes are employed in signal modulation circuits, which are used for transmitting information over long distances. In amplitude modulation (AM) circuits, diodes are used to detect and extract the modulating signal from the carrier wave. In frequency modulation (FM) circuits, varactor diodes are used to control the frequency of the carrier wave. Protection Circuits: Diodes are crucial components in protection circuits, where they safeguard sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes and reverse polarity. Transient voltage suppression diodes, also known as TVS diodes, are used to protect circuits from voltage transients caused by lightning strikes, electrostatic discharge, or other high-voltage events. Additionally, diodes can be used in reverse polarity protection circuits, preventing damage to electronic systems by blocking the reverse flow of current. Logic Gates: Diodes are used in the construction of logic gates, which form the building blocks of digital circuits. By combining diodes with other electronic components, logic gates can perform logical operations such as AND, OR, and NOT. These gates are essential for designing digital systems, including computers, microcontrollers, and integrated circuits. Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): Light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, are a specific type of diode that emits light when current flows through them. LEDs are widely used for various applications, including lighting, displays, indicators, and signage. They offer energy efficiency, long lifespan, and the ability to produce different colors. Diode Lasers: Diode lasers utilize the properties of diodes to emit coherent light. They are used in numerous applications, such as laser pointers, barcode scanners, fiber optic communication, medical equipment, and laser printing. Demodulation: Diodes play a vital role in demodulating signals. In radio receivers, diodes are used for envelope detection, extracting the original modulating signal from an amplitude-modulated carrier wave.Conclusion
Diodes are essential components in electronics, with various types and applications. They are used for rectification, voltage regulation, signal modulation, protection circuits, logic gates, powering LEDs, and diode lasers. Understanding diodes is crucial for anyone interested in electronics. Diodes play a significant role in modern electronics by controlling current flow and performing specific functions.Populer Posts
5SGSMD6K2F40I2LG
Intel
M1A3P600-FGG256I
Microchip Technology
EP3C120F780C8
Intel
APA075-PQG208
Microchip Technology
XC3S50-5CPG132C
AMD
5SGSMD5K3F40I4G
Intel
EP4CGX110DF27I7N
Intel
EP2AGZ300HF40C3G
Intel
AX250-FGG484M
Microchip Technology
1ST210EU2F50I1VG
Intel
ICE5LP2K-SWG36ITR50
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
ICE40UP3K-UWG30ITR1K
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
